16 Feb, 2023
Abstract
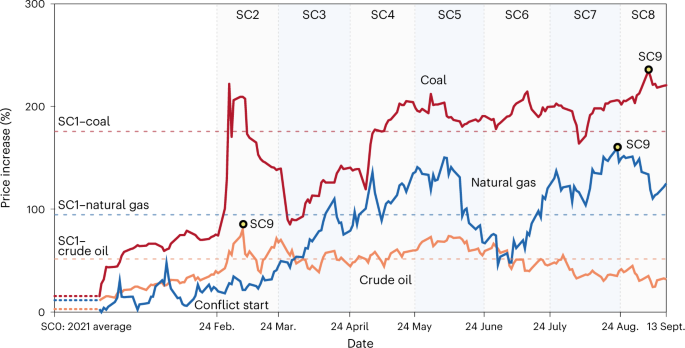
The Russia–Ukraine confict has triggered an energy crisis that directly
afected household energy costs for heating, cooling and mobility and
indirectly pushed up the costs of other goods and services throughout
global supply chains. Here we bridge a global multi-regional input–output
database with detailed household-expenditure data to model the direct and
indirect impacts of increased energy prices on 201 expenditure groups in 116
countries. On the basis of a set of energy price scenarios, we show that total
energy costs of households would increase by 62.6–112.9%, contributing to
a 2.7–4.8% increase in household expenditures. The energy cost burdens
across household groups vary due to diferences in supply chain structure,
consumption patterns and energy needs. Under the cost-of-living pressures,
an additional 78 million–141 million people will potentially be pushed
into extreme poverty. Targeted energy assistance can help vulnerable
households during this crisis. We emphasize support for increased costs of
necessities, especially for food.
....................................................
 www.nature.com
www.nature.com
Abstract
The Russia–Ukraine confict has triggered an energy crisis that directly
afected household energy costs for heating, cooling and mobility and
indirectly pushed up the costs of other goods and services throughout
global supply chains. Here we bridge a global multi-regional input–output
database with detailed household-expenditure data to model the direct and
indirect impacts of increased energy prices on 201 expenditure groups in 116
countries. On the basis of a set of energy price scenarios, we show that total
energy costs of households would increase by 62.6–112.9%, contributing to
a 2.7–4.8% increase in household expenditures. The energy cost burdens
across household groups vary due to diferences in supply chain structure,
consumption patterns and energy needs. Under the cost-of-living pressures,
an additional 78 million–141 million people will potentially be pushed
into extreme poverty. Targeted energy assistance can help vulnerable
households during this crisis. We emphasize support for increased costs of
necessities, especially for food.
....................................................

Burden of the global energy price crisis on households - Nature Energy
The Russia–Ukraine war triggered an energy crisis that affected the cost of many goods and services. Guan et al. model the direct and indirect impacts of increased energy prices across expenditure groups and countries, finding temporary increases in total household energy costs of 63–113% under...







